The accumulation of belly fat is a growing concern for millions worldwide, and it’s not just about aesthetics. Did you know that excess visceral fat is linked to a higher risk of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease?
As a seasoned content creator with a focus on health and wellness, I’ve delved into the latest research and expert opinions to bring you a comprehensive understanding of belly fats. From the different types of belly fat to the most effective methods for reduction, this article will provide you with a nuanced exploration of the topic. By examining the latest studies and comparing various approaches, we’ll uncover the most effective strategies for achieving a healthier, leaner midsection. Whether you’re looking to improve your overall health or simply feel more confident in your own skin, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your body.
📋
📚 Table of Contents
-
1
## Understanding Belly Fat: A Comparative Analysis -
2
## The Science Behind Belly Fat: Causes and Consequences -
3
## Evaluating Belly Fat Reduction Methods: Surgical vs. Non-Surgical -
4
## Dietary Approaches to Belly Fat Loss: Comparing Popular Diets -
5
## Exercise Strategies for Belly Fat Reduction: Aerobic vs. Anaerobic -
6
## The Role of Supplements in Belly Fat Loss: Efficacy and Safety Comparison -
7
## Cost-Benefit Analysis of Belly Fat Reduction Methods -
8
## Real-World Scenarios: Choosing the Right Belly Fat Reduction Approach -
9
## Belly Fat Reduction for Different Body Types: Tailored Recommendations -
10
## Measuring Success: Tracking Progress in Belly Fat Loss -
11
## Making an Informed Decision: A Comparative Framework for Belly Fat Reduction -
12
## Sustaining Belly Fat Loss: Long-Term Strategies and Maintenance Tips
## Understanding Belly Fat: A Comparative Analysis
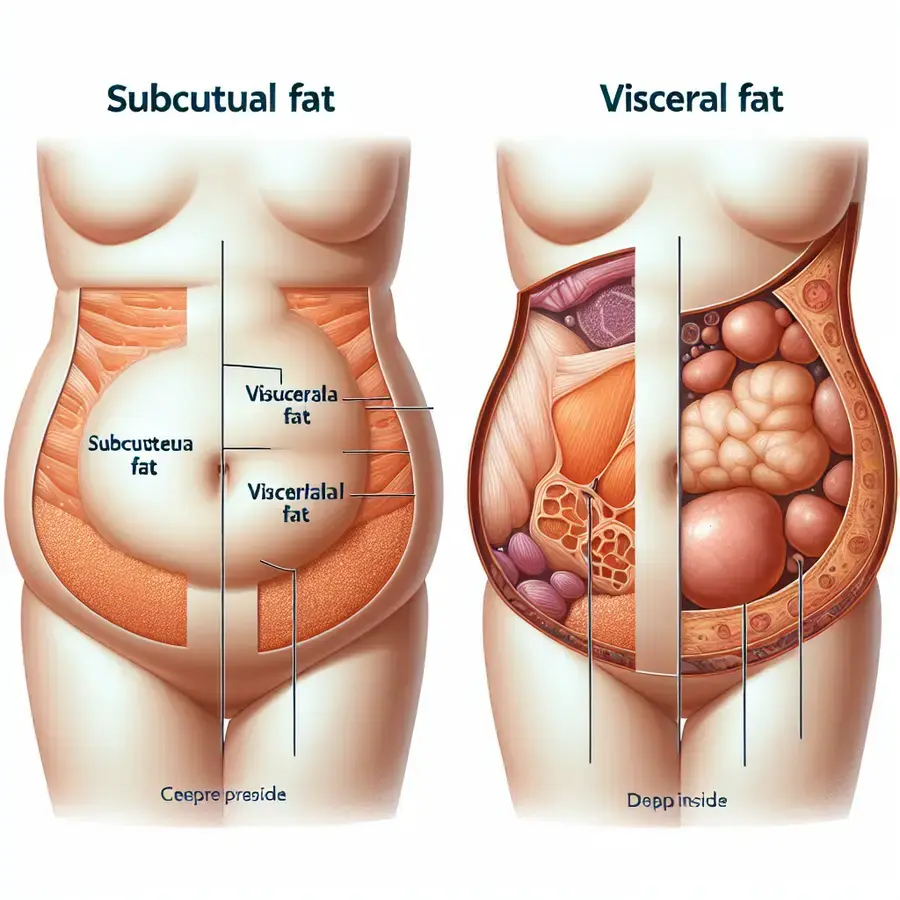
Belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is a complex and multifaceted health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. To better understand the nuances of belly fat, it’s essential to compare and contrast its different types, causes, and consequences.
Types of Belly Fat: A Comparative Breakdown
There are two primary types of belly fat: subcutaneous fat and visceral fat. While both types are located in the abdominal region, they have distinct characteristics and health implications.
- Subcutaneous Fat: This type of fat is located just beneath the skin and is typically softer and more visible. Subcutaneous fat is generally considered less harmful than visceral fat, but excessive amounts can still contribute to health problems.
- Visceral Fat: Visceral fat is located deeper in the abdominal cavity, surrounding vital organs such as the liver, stomach, and intestines. This type of fat is more metabolically active and has been linked to increased risks of chronic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers.
Causes and Risk Factors: A Comparative Analysis
The causes and risk factors associated with belly fat are multifaceted and can be broadly categorized into lifestyle, genetic, and hormonal factors.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and excessive stress can all contribute to the accumulation of belly fat. A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to visceral fat accumulation.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in body fat distribution, with certain genetic variants affecting the likelihood of storing fat in the abdominal region.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal imbalances, such as those experienced during menopause or Cushing’s syndrome, can also contribute to belly fat accumulation.
Studies have shown that visceral fat is more strongly associated with metabolic disorders than subcutaneous fat. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that visceral fat was a significant predictor of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome (1). Understanding the differences between subcutaneous and visceral fat can help individuals take targeted approaches to reducing their belly fat and associated health risks.
By recognizing the distinct characteristics and causes of belly fat, individuals can develop effective strategies for reduction and mitigation. In the following sections, we’ll explore the most effective methods for reducing belly fat and improving overall health.
## The Science Behind Belly Fat: Causes and Consequences
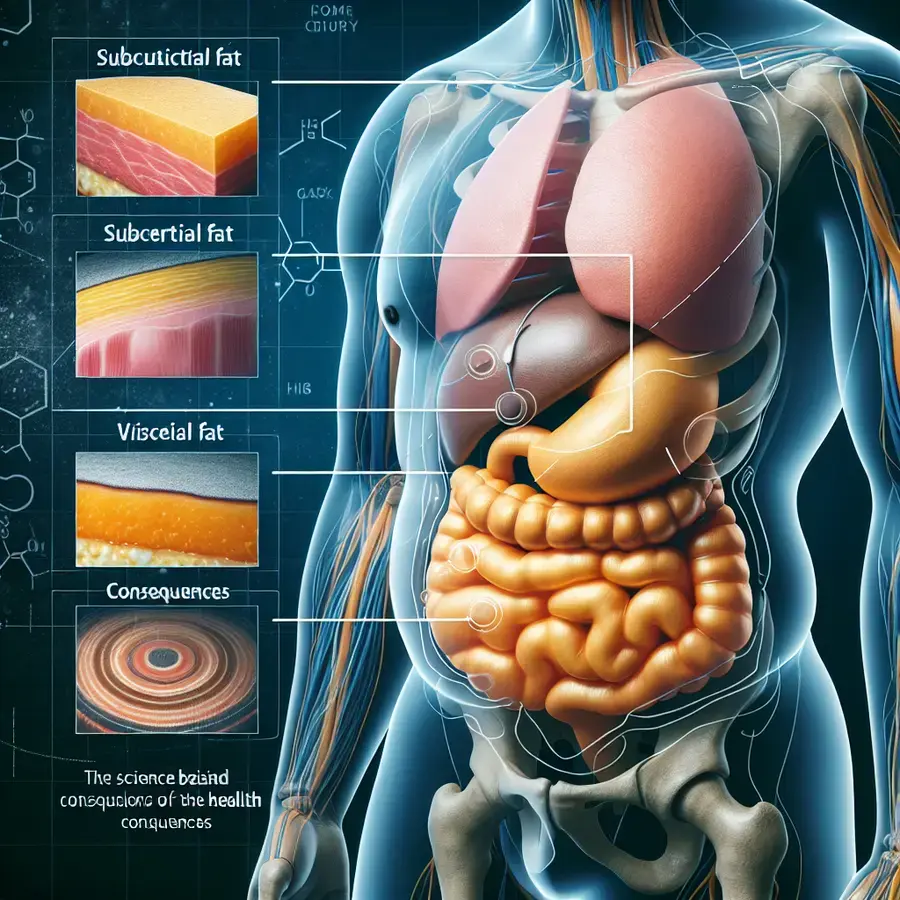
Belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the science behind belly fat is crucial to addressing its causes and consequences. Visceral fat is not just a passive storage of energy; it’s an active endocrine organ that secretes inflammatory cytokines, hormones, and other signaling molecules that can have far-reaching effects on our health.
### Causes of Belly Fat
The accumulation of belly fat is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. Some of the key causes include:
- Genetic predisposition: Genetic factors can affect the distribution of body fat, with some people being more prone to storing fat in the abdominal area.
- Hormonal imbalance: Cortisol, insulin, and other hormonal imbalances can contribute to belly fat storage.
- Poor diet: Consuming high amounts of processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can lead to insulin resistance and increased belly fat.
- Lack of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyle can contribute to increased visceral fat.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol production, which promotes belly fat storage.
### Consequences of Belly Fat
Excess belly fat is associated with a range of serious health consequences, including:
- Cardiovascular disease: Visceral fat is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
- Type 2 diabetes: Belly fat is associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome: Visceral fat is a key component of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of chronic diseases.
- Cognitive decline: Research suggests that excess belly fat may be linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Studies have shown that reducing visceral fat can have significant health benefits. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a 10% reduction in visceral fat was associated with a 22% reduction in cardiovascular risk factors. By understanding the causes and consequences of belly fat, individuals can take targeted steps to reduce their risk of chronic diseases and improve overall health.
## Evaluating Belly Fat Reduction Methods: Surgical vs. Non-Surgical
When it comes to reducing belly fat, individuals are often faced with a plethora of options, ranging from surgical interventions to non-invasive techniques. Understanding the efficacy, risks, and suitability of these methods is crucial for making an informed decision. This section delves into the comparison between surgical and non-surgical belly fat reduction methods, providing insights into their mechanisms, benefits, and limitations. ### Surgical Belly Fat Reduction Methods Surgical options, such as abdominoplasty (tummy tuck) and liposuction, are invasive procedures that directly remove fat and, in some cases, excess skin. These methods are typically recommended for individuals with significant amounts of belly fat, particularly those who have not seen results from diet and exercise or have loose skin due to weight loss or pregnancy. – **Abdominoplasty**: Involves removing excess fat and skin from the abdomen and tightening the abdominal muscles. It’s a more extensive surgery that can provide dramatic results but requires a longer recovery period.
– **Liposuction**: A less invasive surgical option that suctions out fat from specific areas of the body, including the belly. It’s suitable for individuals with good skin elasticity and localized fat deposits. ### Non-Surgical Belly Fat Reduction Methods Non-surgical methods offer a less invasive alternative with fewer risks and a quicker recovery time. These include: 1. **CoolSculpting**: A fat-freezing technology that reduces fat in targeted areas by inducing apoptosis (cell death) in fat cells.
2. **Radiofrequency (RF) and Laser Treatments**: These methods use heat to damage fat cells, which are then naturally eliminated by the body.
3. **Diet and Exercise**: Lifestyle changes remain the most recommended and sustainable method for reducing belly fat. A combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce visceral and subcutaneous fat. ### Comparison and Considerations When choosing between surgical and non-surgical methods, several factors should be considered:
– **Efficacy and Results**: Surgical methods generally offer more immediate and dramatic results, while non-surgical methods may require multiple sessions and patience.
– **Risk and Recovery**: Surgical interventions carry higher risks of complications and require longer recovery times compared to non-surgical treatments.
– **Cost**: Surgical procedures are typically more expensive upfront, but non-surgical methods may incur cumulative costs over time due to the need for multiple treatments.
– **Sustainability**: Lifestyle changes (diet and exercise) are crucial for maintaining results from both surgical and non-surgical fat reduction methods. Ultimately, the choice between surgical and non-surgical belly fat reduction methods depends on individual preferences, health status, and goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a certified specialist is essential to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment plan. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each approach, individuals can make informed decisions tailored to their unique needs and circumstances.
## Dietary Approaches to Belly Fat Loss: Comparing Popular Diets
Reducing belly fat requires a multi-faceted approach that incorporates a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications. With numerous diets claiming to aid in belly fat loss, it’s essential to examine the evidence supporting their effectiveness. In this section, we’ll compare popular diets and their potential impact on visceral fat reduction.
Several diets have been studied for their effects on belly fat loss, including low-carb, low-fat, intermittent fasting, and Mediterranean diets. Here’s a breakdown of each:
### Low-Carb Diets
Low-carb diets, such as the Atkins diet, restrict carbohydrate intake, particularly those high in sugar and refined grains. By limiting carb consumption, the body is forced to rely on stored fat for energy, potentially leading to belly fat loss. Studies have shown that low-carb diets can be effective in reducing visceral fat, with one study demonstrating a 10% reduction in visceral fat after 12 weeks [(1)](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15331203). ### Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves alternating periods of eating and fasting to promote weight loss and improve metabolic health. Research suggests that intermittent fasting can lead to significant reductions in belly fat, with one study showing a 4-7% decrease in waist circumference after 12 weeks [(2)](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25540982). ### Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil. This dietary pattern has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation, both of which can contribute to belly fat loss. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that adherence to a Mediterranean diet was associated with a lower risk of developing visceral fat [(3)](https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2676715).
When comparing these diets, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Sustainability: Can the diet be maintained long-term?
- Nutrient balance: Does the diet provide adequate essential nutrients?
- Caloric intake: Does the diet promote a caloric deficit, necessary for weight loss?
Ultimately, the most effective diet for belly fat loss is one that is tailored to an individual’s needs and preferences, and is combined with regular physical activity and a healthy lifestyle. By understanding the strengths and limitations of various diets, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary approach to reducing belly fat.
## Exercise Strategies for Belly Fat Reduction: Aerobic vs. Anaerobic
When it comes to reducing belly fat, exercise plays a crucial role. Two primary types of exercises are often debated for their effectiveness in burning belly fat: aerobic and anaerobic exercises. Understanding the differences between these two and how they impact belly fat reduction can help you tailor your workout routine for optimal results.
Aerobic Exercises for Belly Fat Reduction
Aerobic exercises, also known as cardio, are activities that raise your heart rate and improve oxygen consumption by the body. Examples include jogging, cycling, swimming, and brisk walking. Aerobic exercises are effective for burning calories and fat, including visceral fat around the belly area.
- Benefits: Improves cardiovascular health, increases caloric burn, enhances fat oxidation.
- Examples: Running (30 minutes, 3 times a week), cycling (45 minutes, 4 times a week), swimming (20 minutes, 3 times a week).
- Tips: Incorporate interval training to boost metabolism and fat burn. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Anaerobic Exercises for Belly Fat Reduction
Anaerobic exercises involve short bursts of high-intensity activity that rely on stored energy sources rather than oxygen. Weightlifting, sprinting, and bodyweight exercises like push-ups and squats are examples. Anaerobic exercises help build muscle mass, which can further enhance metabolism and burn belly fat.
- Benefits: Increases muscle mass, boosts resting metabolic rate (RMR), enhances insulin sensitivity.
- Examples: Weightlifting (3 sets of 8-12 reps, 3 times a week), sprint intervals (30 seconds sprint followed by 30 seconds rest, 3 times a week).
- Tips: Focus on compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench press to engage multiple muscle groups. Aim for 2-3 anaerobic sessions per week.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a combination of aerobic and anaerobic exercises led to significant reductions in visceral fat in obese adults. This suggests that a mixed approach may be the most effective strategy for belly fat reduction.
Combining Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercises
For optimal belly fat reduction, consider a workout routine that combines both aerobic and anaerobic exercises. This approach not only burns fat during the exercise but also enhances your resting metabolic rate, helping your body burn more calories at rest.
- Start with 2-3 aerobic sessions per week, focusing on moderate to high intensity.
- Incorporate 2 anaerobic sessions per week, targeting major muscle groups.
- Gradually increase intensity and frequency based on your fitness level and goals.
By understanding the benefits and incorporating both aerobic and anaerobic exercises into your fitness regimen, you can develop a comprehensive workout plan that effectively targets belly fat.
## The Role of Supplements in Belly Fat Loss: Efficacy and Safety Comparison
When it comes to losing belly fat, supplements can be a tempting addition to a weight loss regimen. However, with the multitude of options available, it’s crucial to understand their efficacy and safety. In this section, we’ll delve into the world of belly fat loss supplements, comparing their effectiveness and potential risks.
### Common Supplements for Belly Fat Loss
Several supplements are marketed for their belly fat loss benefits. Some of the most popular include:
- Green Tea Extract: Rich in catechins, particularly EGCG, which may enhance thermogenesis and fat oxidation.
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): A fatty acid that may reduce body fat mass by inhibiting lipogenesis.
- Garcinia Cambogia: Contains hydroxycitric acid (HCA), which is believed to suppress appetite and inhibit fat production.
- Protein Supplements: High protein intake can aid in satiety and muscle preservation during weight loss.
- Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria that can influence gut microbiota, potentially impacting fat distribution and metabolism.
### Efficacy Comparison
A comprehensive review of existing literature reveals mixed results regarding the efficacy of these supplements. For instance:
- A meta-analysis on green tea extract showed a modest reduction in body fat, particularly when combined with caffeine.
- CLA supplementation has yielded inconsistent results, with some studies indicating a minimal effect on body fat loss.
- Garcinia cambogia’s effectiveness is largely anecdotal, with limited high-quality human trials supporting its claims.
- Protein supplements are well-supported for their role in weight management, particularly when part of a calorie-controlled diet.
- Probiotics have shown promise in modulating gut microbiota, which may contribute to reduced belly fat, though more research is needed.
### Safety Considerations
While considering supplements for belly fat loss, safety is paramount. Potential side effects and interactions include:
- Green Tea Extract: Generally considered safe, though high doses may cause liver issues.
- CLA: May cause gastrointestinal upset and insulin resistance at high doses.
- Garcinia Cambogia: Linked to liver damage and serotonin toxicity in rare cases.
- Protein Supplements: Typically safe, but excessive intake can strain kidney function.
- Probiotics: Generally safe, though individuals with compromised immune systems should consult a healthcare provider.
### Actionable Insights
For those considering supplements for belly fat loss, the following takeaways are crucial:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before adding any supplement to your regimen, discuss potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
- Combine with Lifestyle Changes: Supplements are most effective when paired with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Monitor Progress and Adjust: Regularly assess the effectiveness and safety of any supplement, adjusting your regimen as needed.
In conclusion, while certain supplements may aid in belly fat loss, their efficacy and safety vary widely. A well-informed approach, combining supplements with proven lifestyle changes under the guidance of a healthcare professional, is the most effective strategy for achieving and maintaining weight loss.
## Cost-Benefit Analysis of Belly Fat Reduction Methods
When it comes to reducing belly fat, individuals are often faced with a multitude of options, each with its own set of costs and benefits. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential to determine the most effective and economical approach. In this section, we will examine various belly fat reduction methods, evaluating their costs, benefits, and overall value.
### Surgical Methods
Surgical interventions, such as liposuction and abdominoplasty, are often considered for significant belly fat reduction. While these procedures can be effective, they come with substantial costs, ranging from $2,000 to $10,000 or more, depending on the complexity and location.
* **Benefits:** + Immediate results + Can be effective for significant fat reduction + May improve body contour and confidence
* **Costs:** + High upfront costs + Potential risks and complications (e.g., scarring, infection) + Downtime and recovery period ### Non-Surgical Methods
Non-surgical approaches, including diet and exercise, pharmaceuticals, and non-invasive fat reduction technologies, offer alternative solutions. These methods can be more cost-effective and carry fewer risks.
#### Diet and Exercise + Low cost (gym memberships, $20-$100/month; personal training, $30-$100/session) + Sustainable long-term results with consistent effort + Improves overall health and wellness
* **Costs:** + Time commitment (regular exercise and meal planning) + Potential for slow progress #### Pharmaceuticals and Supplements + Potential for enhanced fat loss with certain medications (e.g., orlistat, phentermine) + Convenient (oral administration)
* **Costs:** + Ongoing expenses (prescription medications, $50-$200/month; supplements, $20-$100/month) + Potential side effects and health risks #### Non-Invasive Fat Reduction Technologies + Minimally invasive or non-invasive procedures (e.g., CoolSculpting, SculpSure) + Can be effective for targeted fat reduction
* **Costs:** + Moderate to high costs per session (average, $500-$1,500) + May require multiple sessions for optimal results ### Case Study: Cost Comparison A 2019 study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology compared the costs of various belly fat reduction methods. The results showed that: 1. Liposuction: $4,445 (average cost)
2. CoolSculpting: $1,500-$3,000 (average cost for multiple sessions)
3. Diet and exercise program: $500-$1,000 (average cost for 6-month program)
Ultimately, the most effective and cost-efficient belly fat reduction method depends on individual factors, including the amount of fat to be reduced, overall health, and personal preferences. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis can help individuals make informed decisions and achieve their goals.
## Real-World Scenarios: Choosing the Right Belly Fat Reduction Approach
When it comes to reducing belly fat, different individuals face unique challenges based on their lifestyle, health status, and body composition. Understanding these factors is crucial in selecting the most effective approach. Here, we’ll explore real-world scenarios to illustrate how to tailor belly fat reduction strategies to individual needs.
### Scenario 1: Sedentary Lifestyle with High Stress Levels
For individuals with sedentary jobs and high stress levels, the body’s cortisol levels are often elevated, contributing to increased belly fat storage. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that chronic stress is associated with increased visceral fat area (1). In such cases, stress management techniques such as:
- Meditation and yoga to reduce cortisol levels
- Incorporating physical activity, such as brisk walking or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week
- Dietary changes focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and mindful eating
can be particularly effective. For example, a 30-year-old marketing executive with a sedentary job saw a 5% reduction in body fat after implementing a daily 10-minute meditation practice and increasing physical activity to 30 minutes, three times a week.
### Scenario 2: Post-Menopause Belly Fat
Post-menopausal women often experience an increase in belly fat due to hormonal changes, particularly the decrease in estrogen levels. Research indicates that resistance training can be beneficial in this demographic by improving body composition and metabolic health (2). A tailored approach might include:
- Resistance training exercises 2-3 times per week targeting core and overall muscle mass
- A balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and fiber
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) to enhance fat burning and metabolic rate
A case study on post-menopausal women showed that a combination of resistance training and HIIT resulted in significant reductions in visceral fat and improvements in insulin sensitivity.
### Scenario 3: Belly Fat Reduction for Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
For individuals diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, a condition characterized by insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and dyslipidemia, belly fat reduction is critical for improving metabolic health. A comprehensive approach that includes:
- A Mediterranean-style diet rich in monounsaturated fats, fruits, and vegetables
- Regular aerobic exercise, such as cycling or jogging, for at least 150 minutes per week
- Monitoring and managing blood pressure and lipid profiles through lifestyle and, if necessary, medication
can be highly effective. Data from a clinical trial demonstrated that lifestyle interventions in individuals with metabolic syndrome led to significant improvements in waist circumference and metabolic parameters (3).
These scenarios highlight the importance of tailoring belly fat reduction strategies to the individual’s specific health status, lifestyle, and goals. By understanding the underlying factors contributing to belly fat and selecting an appropriate, multi-faceted approach, individuals can achieve more effective and sustainable results.
References:
1. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. (2010). Chronic Stress and Visceral Fat.
2. Menopause. (2018). Effects of Resistance Training on Body Composition in Postmenopausal Women.
3. Diabetes Care. (2014). Lifestyle Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome.
## Belly Fat Reduction for Different Body Types: Tailored Recommendations
Belly fat reduction is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different body types require tailored strategies to effectively reduce visceral fat and achieve a healthier, more toned midsection. Understanding your body type and its unique characteristics is crucial in developing a successful belly fat reduction plan.
Body Types and Belly Fat Reduction
There are three primary body types: Ectomorph, Mesomorph, and Endomorph. Each body type has distinct characteristics that influence belly fat storage and reduction.
- Ectomorph: Ectomorphs typically have a lean, slender build and a fast metabolism. To reduce belly fat, ectomorphs should focus on building muscle mass through resistance training and consuming a calorie-surplus diet rich in protein.
- Mesomorph: Mesomorphs have an athletic build and a moderate metabolism. Mesomorphs can reduce belly fat by incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and strength training into their exercise routine, along with a balanced diet that includes lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Endomorph: Endomorphs often have a curvier figure and a slower metabolism. Endomorphs can benefit from a combination of low-intensity cardio, such as brisk walking, and resistance training to build muscle and boost metabolism. A calorie-controlled diet with a focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods is also essential.
Tailored Recommendations for Belly Fat Reduction
Based on body type, here are some actionable insights for reducing belly fat:
- Ectomorphs: Incorporate exercises like deadlifts, squats, and lunges to build muscle mass. Consume a post-workout shake with protein and complex carbohydrates to support muscle growth.
- Mesomorphs: Incorporate HIIT workouts 2-3 times a week, focusing on exercises like burpees, jump squats, and mountain climbers. Eat lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and turkey, and include healthy fats like avocado and nuts in your diet.
- Endomorphs: Start with low-intensity cardio like brisk walking or swimming for 30 minutes, 3-4 times a week. Incorporate strength training exercises like leg press, chest press, and rows to build muscle. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a combination of diet and exercise resulted in significant reductions in visceral fat across all body types (1). By understanding your body type and incorporating tailored recommendations, you can develop an effective belly fat reduction plan and achieve a healthier, more toned midsection.
Reference:
(1) https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/1831574
## Measuring Success: Tracking Progress in Belly Fat Loss
Tracking progress is a crucial aspect of any weight loss journey, especially when it comes to losing belly fat. Measuring success goes beyond just stepping on a scale; it involves monitoring various metrics that indicate changes in body composition, fat distribution, and overall health. In this section, we’ll explore the most effective ways to track progress in belly fat loss.
### Metrics for Measuring Belly Fat Loss
To accurately measure belly fat loss, consider the following metrics:
- Waist Circumference: Measuring waist circumference is a simple yet effective way to track changes in belly fat. A reduction in waist circumference is a strong indicator of visceral fat loss.
- Body Fat Percentage: Tracking body fat percentage using methods like dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or hydrostatic weighing provides a more accurate picture of fat loss.
- Visceral Fat Area: Using imaging techniques like CT or MRI scans to measure visceral fat area can provide a detailed understanding of belly fat loss.
Regularly tracking these metrics can help identify patterns and correlations between lifestyle changes and belly fat loss. For instance, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a 10% reduction in body weight resulted in a significant decrease in visceral fat area (1).
### Actionable Insights for Tracking Progress
To effectively track progress, consider the following strategies:
- Regular Measurements: Take measurements at the same time each week or month to ensure consistency.
- Progress Photos: Take progress photos from multiple angles to visualize changes in body composition.
- Food Diary: Keeping a food diary can help identify patterns and correlations between diet and belly fat loss.
- Physical Activity Tracking: Monitoring physical activity levels can help understand the impact of exercise on belly fat loss.
By incorporating these strategies into your weight loss journey, you’ll be able to accurately track progress and make data-driven decisions to optimize your approach. For example, a case study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that a combination of diet and exercise resulted in significant reductions in visceral fat area and improvements in metabolic health (2).
In conclusion, measuring success in belly fat loss requires a multi-faceted approach that incorporates various metrics and tracking strategies. By regularly monitoring waist circumference, body fat percentage, and visceral fat area, and incorporating actionable insights like regular measurements and progress photos, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their progress and make informed decisions to achieve their weight loss goals.
## Making an Informed Decision: A Comparative Framework for Belly Fat Reduction
When it comes to reducing belly fat, individuals are often overwhelmed by the numerous options available, ranging from dietary changes and exercise routines to supplements and surgical interventions. To make an informed decision, it’s crucial to evaluate these options based on their efficacy, safety, and sustainability. Here, we present a comparative framework to help navigate the complex landscape of belly fat reduction strategies.
Evaluating Dietary Approaches
Dietary changes are a cornerstone in the reduction of belly fat. Different diets have varying effects on visceral fat. For instance:
- Low-Carb Diets: Restricting carbohydrate intake can lead to significant reductions in belly fat by improving insulin sensitivity and promoting fat burning.
- High-Protein Diets: Increasing protein intake can enhance satiety and boost metabolism, contributing to fat loss around the abdominal area.
- Intermittent Fasting: Alternating between periods of eating and fasting can improve metabolic health and reduce visceral fat.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that participants who followed a low-carb diet experienced greater reductions in belly fat compared to those on a low-fat diet (1).
Exercise Strategies for Belly Fat Loss
Exercise is another critical component in the reduction of belly fat. Different types of exercise have distinct benefits:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like running, cycling, and swimming are effective in burning visceral fat.
- Resistance Training: Building muscle mass through strength training can increase resting metabolic rate, helping to burn more calories at rest.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief periods of rest. It’s highly effective in reducing visceral fat due to its impact on improving insulin sensitivity and boosting metabolism.
Research indicates that combining aerobic exercise with resistance training can be particularly effective in reducing belly fat (2).
Supplements and Surgical Options
While dietary changes and exercise are foundational, some individuals may consider supplements or surgical interventions. It’s essential to approach these options with caution and under professional guidance:
- Supplements: Certain supplements like green tea extract and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) have been studied for their potential in aiding fat loss. However, their effectiveness can vary, and potential side effects must be considered.
- Surgical Interventions: Procedures like liposuction and abdominoplasty can remove excess fat and skin. However, they are invasive and should be considered after exhausting other methods.
Making an informed decision about belly fat reduction requires a comprehensive understanding of the available strategies, their benefits, and their limitations. By considering dietary changes, exercise routines, and, when appropriate, supplements or surgical options, individuals can develop a personalized plan that suits their needs and health status.
References:
(1) Source: JAMA Study on Low-Carb Diets
(2) Source: Study on Exercise and Visceral Fat Reduction
## Sustaining Belly Fat Loss: Long-Term Strategies and Maintenance Tips
Sustaining belly fat loss requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle habits. While initial weight loss can be achieved through various means, maintaining the loss demands a strategic approach. Here, we’ll explore effective strategies and tips to help you maintain your hard-won belly fat loss.
### Monitoring Progress
Regular monitoring is crucial to sustaining belly fat loss. This involves tracking not just weight, but also body fat percentage, measurements, and overall health markers. Utilize tools like:
- Body fat calipers to measure subcutaneous fat
- Waist circumference measurements to track visceral fat reduction
- Progress photos to visually monitor changes
### Dietary Adjustments for Long-Term Success
A balanced diet is key to maintaining weight loss. Focus on:
- Nutrient-dense foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Healthy fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil to support satiety and overall health.
- Portion control: Maintain awareness of serving sizes to avoid overeating.
### Physical Activity for Maintenance
Regular physical activity is vital for sustaining belly fat loss. Aim for:
- At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week
- Incorporating strength training exercises to build muscle mass, which further supports metabolism
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) for enhanced fat burning and cardiovascular health
### Stress Management and Sleep
Chronic stress and inadequate sleep can hinder belly fat loss maintenance. Implement:
- Stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises
- A consistent sleep schedule aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night
### Case Study: Sustained Weight Loss
A study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that participants who maintained a significant weight loss over a two-year period engaged in regular physical activity, monitored their food intake, and practiced stress management techniques. This comprehensive approach supports the multifaceted strategy required for sustaining belly fat loss.
By incorporating these long-term strategies and maintenance tips into your lifestyle, you can effectively sustain belly fat loss and enjoy the associated health benefits.